04
Jan
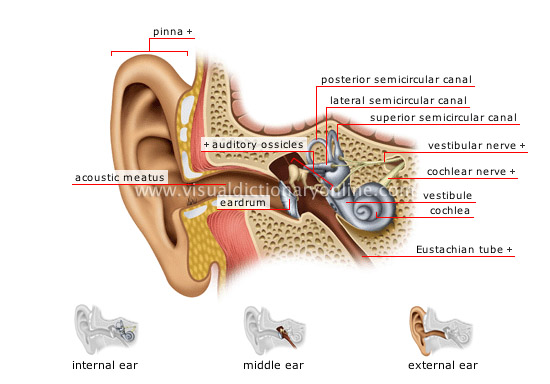
Ear And Its Functions
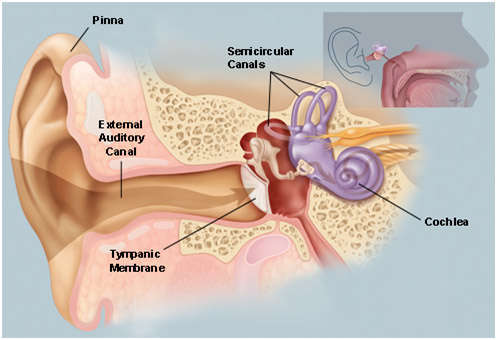
Each ear is divided into three sections:
- The outer ear
- The middle ear
- The inner ear.
The Outer Ear
- It’s the external part of the ear which consists of pinna.
- Pinna is made up of a yellow cartilage.
- The outer ear collects sounds and funnel into the Sound funnels through the pinna into the external auditory canal.
The middle ear
- The middle ear begins at the end of the external auditory canal with the tympanic membrane, or eardrum.
- It vibrates in response to sound waves.
- Middle ear contains three tiny bones known as the auditory ossicles, which transfers the vibrations of the tympanic membrane.
- The Eustachian tube joins the tympanic cavity with the nasal cavity, allowing pressure to equalize between the middle ear and throat.
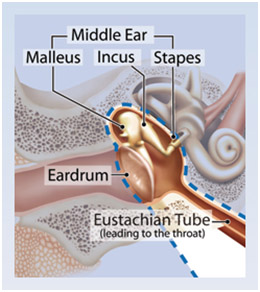
Tympanic Membrane
- It’s also called as the ear drum.
- It receives sound vibrations from the environment and transmits them to the ossicles.
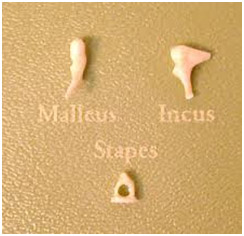
Ossicles
- Malleus (hammer)
- Incus (anvil)
- Stapes (stirrup)
- The ossicles directly couple sound energy from the ear drum to the cochlea.
- Stapes or stirrup is the smallest bone in the human body.
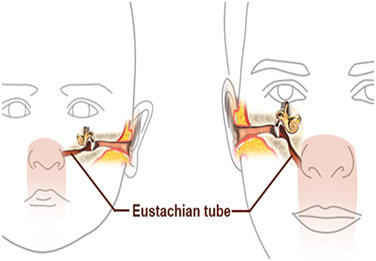
Eustachian Tube
- Eustachian tube,also called Auditory Tube,
- It links the Nasopharynx to the middle ear.
- It helps to equalize the pressure between the middle ear and the outer ear.
- It is covered by one side of the ear drum.
- The function of the auditory tube is ventilation of the middle ear and maintenance of equalized pressure on both sides of the ear drum.
- Closed at most times, the tube opens during swallowing.
- Eustachian tube is to drain any accumulated secretions, infection, or debris from the middle ear space.
For Children:
- Smaller
- Horizontal
- Softer
- Shorter (9mm,0.36 inches)
For Adults:
- Larger
- More vertical
- Stiffer
- Longer (18mm, 0.71 inches)
The inner ear
- The inner ear is the final section of the ear.
- It receives vibrations from the outer and middle ear.
- It converts these vibrations into nerve impulses and it goes to the brain.
- It serves as the body’s balance
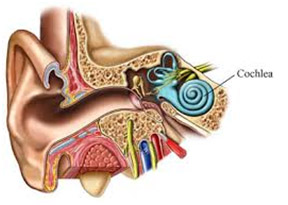
- Within the inner ear is the cochlea that contains delicate hair cells.
- Cochlea serves as the body’s microphone.
- The shape of this canal somewhat resembles a snail shell.
The cochlea has two fluid filled sections.
- Perilymph
- Endolymph
The organ of Corti is the sensory receptor inside the cochlea which holds the hair cells, the nerve receptors for hearing.
The outer ear captures the sound from the environment and the middle ear converts that sounds in to mechanical forces.
The cochlea takes the fluid vibration of sounds from the surrounding semicircular ducts and translates them into signals that are sent to the brain by nerves like the vestibular nerve and cochlear nerve.

0 comments